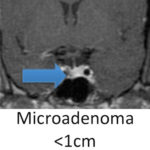
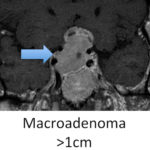
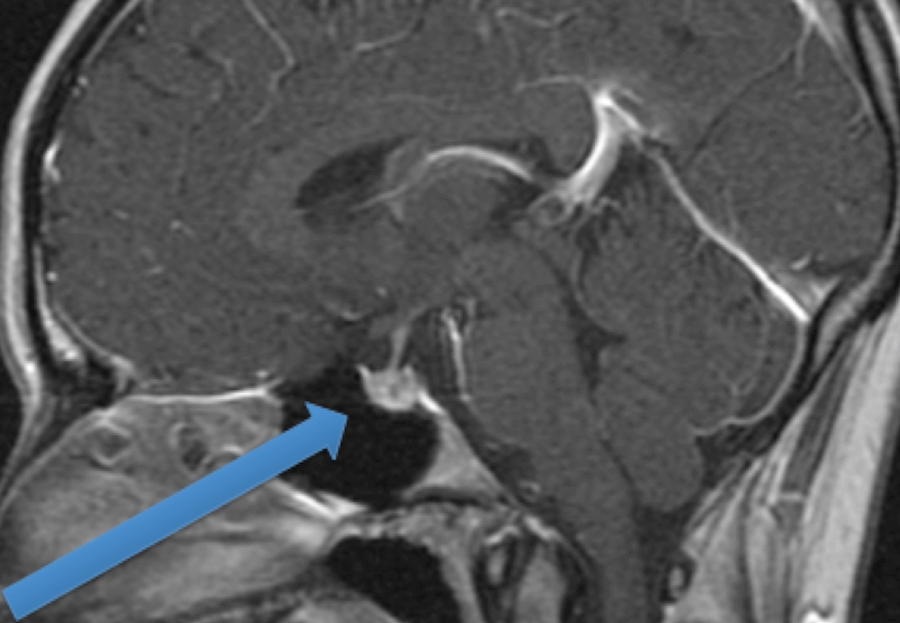
Majority of pituitary adenomas are small and do not require any treatment.
The pituitary gland sits at the base of the skull and can form a tumor called a pituitary adenoma. About 10-15% of adult brain tumors that start in the brain are pituitary adenomas. It is estimated that asymptomatic pituitary tumors may be present in up to 25% of people.